- Formation : 4 April 1949 (75 years ago)
- Type : Military alliance
- Headquarters : Brussels, Belgium
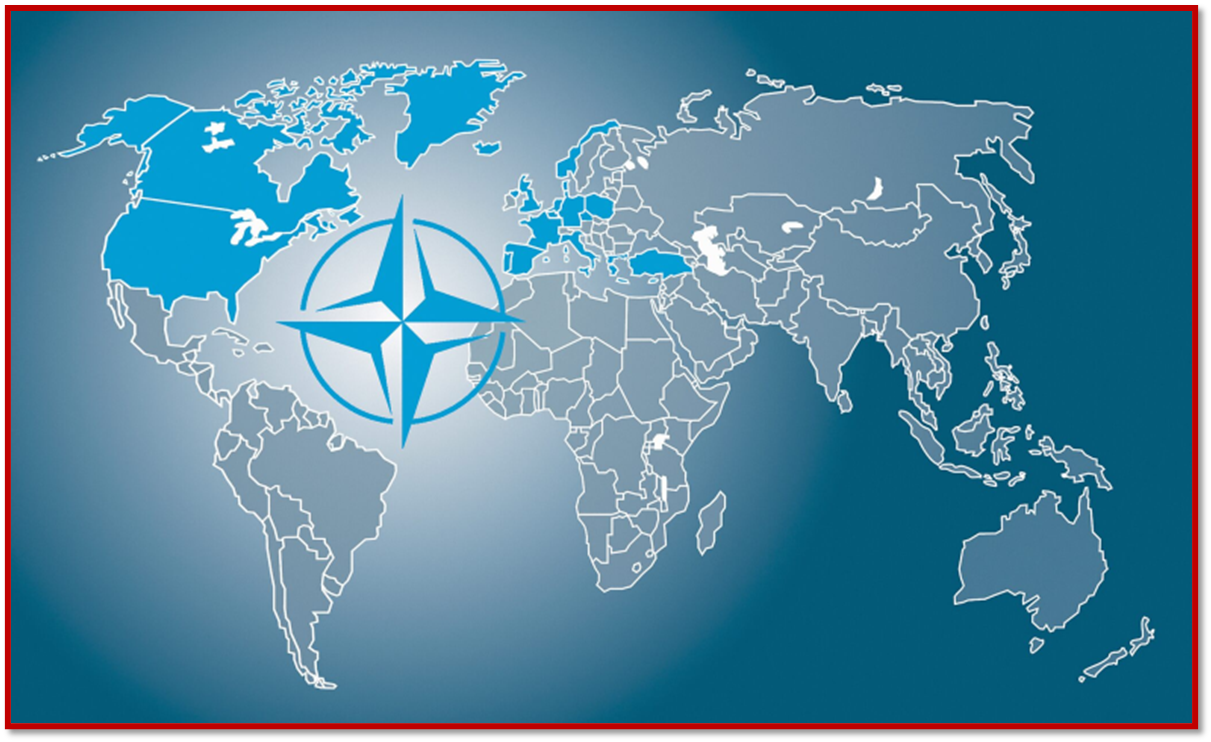
- Membership : 32 states (Sweden became the 32nd member on March 7, 2024)
About:
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is an intergovernmental military alliance formed in 1949.
- It was established with the primary goal of providing collective defence against potential aggression, particularly from the Soviet Union during the Cold War era.
- Over the years, NATO has evolved to address a range of security challenges beyond its original mandate.
History:
- Formation: NATO was established on April 4, 1949, with the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty in Washington, D.C. by 12 founding member countries from Europe and North America.
- Cold War Era: During the Cold War, NATO served as a deterrent against Soviet expansionism, with the US providing significant military support to its European allies.
- Post-Cold War: After the collapse of the Soviet Union, NATO expanded its focus to include crisis management, conflict prevention, and cooperative security efforts.
Membership:
- Original Members: The original 12 founding members of NATO were Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- Expansion: NATO has expanded since its founding, with new member countries joining in multiple rounds. The alliance currently consists of 32 member countries.
Mission and Objectives:
- Collective Defence: NATO's primary mission is collective defence, as outlined in Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty. This article stipulates that an attack on one member country will be considered an attack on all, and the members will respond collectively.
- Crisis Management: In addition to collective defence, NATO engages in crisis management activities, including conflict prevention, peacekeeping, and stabilisation efforts in various regions around the world.
Structure:
- Political Leadership: The North Atlantic Council (NAC) serves as NATO's principal political decision-making body, composed of ambassadors from all member countries.
- Military Command Structure: NATO's military command structure includes Strategic Commands (e.g., Allied Command Operations) responsible for operational planning and execution, as well as Regional Commands and Force Headquarters.
- Integrated Military Forces: NATO maintains integrated military forces, allowing member countries to contribute personnel and assets to collective defence efforts under NATO command.
Note:
India maintains a nuanced stance between NATO and Russia, balancing strategic interests with both while emphasising non-alignment and bilateral cooperation in defence and economic spheres.